Supply Chain Disruptions: How US Businesses Can Prepare
Supply chains are the lifeblood of global commerce, ensuring the smooth movement of goods, materials, and services across industries. However, disruptions in supply chains can have far-reaching consequences, affecting production, delivery, and ultimately, consumer satisfaction. From natural disasters to pandemics, geopolitical tensions, and cyberattacks, supply chain disruptions are inevitable and unpredictable, making it crucial for businesses to understand the causes, impacts, and strategies to mitigate their effects.
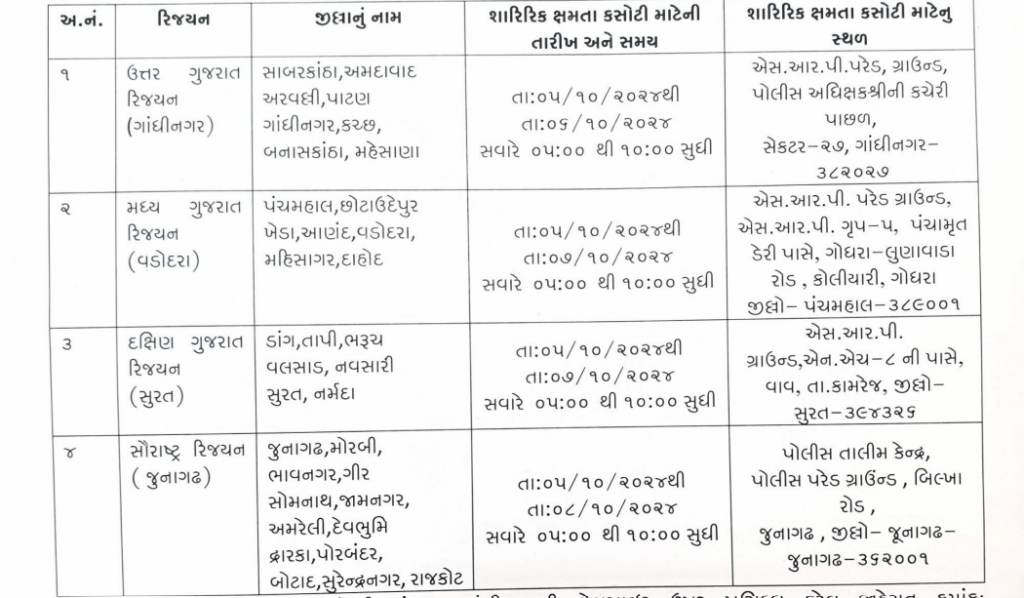
ગુજરાત ફોરેસ્ટ ગાર્ડ શારીરિક કસોટી તારીખ જાહેર: વનરક્ષક કોલ લેટર ડાઉનલોડ તારીખ જાહેર, જુઓ સંપૂર્ણ માહિતી

ગુજરાત ફોરેસ્ટ ગાર્ડ શારીરિક કસોટી તારીખ જાહેર
વનરક્ષક વર્ગ-૩ સંવર્ગના ભરતી નિયમો / પરીક્ષા નિયમો મુજબ ઉમેદવારોએ માટે શારીરિક ક્ષમતા કસોટી પાસ કરવી જરૂરી છે. જે ઉમેદવાર આ માટે શારીરિક ક્ષમતા કસોટીમાં ઉપસ્થિત રહેશે નહિ તેઓને બીજી તક આપવામાં આવશે નહિ અને તેઓની ઉમેદવારી રદ્દ થશે. જેની દરેક ઉમેદવારે નોંધ લેવી.
મહત્વપૂર્ણ લિંક :
| શારીરિક કસોટી તારીખ ની જાહેરાત | અહીં ક્લિક કરો |
In this article, we will explore the various causes of supply chain disruptions, their potential consequences, and the key steps businesses can take to build resilience in their supply chains.
What Are Supply Chain Disruptions?
Supply chain disruptions refer to any unforeseen events or situations that hinder the normal flow of goods, materials, or services within a supply chain. These disruptions can occur at any point in the chain, from the procurement of raw materials to the delivery of finished products to end customers. Disruptions can be short-term, such as a temporary production delay, or long-term, causing significant and prolonged challenges for businesses.
Common Causes of Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions can arise from various internal and external factors. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Natural Disasters
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and tsunamis can cause widespread destruction to infrastructure, transportation networks, and manufacturing facilities. These events can halt production, delay shipments, and disrupt the availability of raw materials, affecting the entire supply chain.
For example, the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan severely impacted global supply chains, particularly in the automotive and electronics industries. The disaster led to significant production delays, affecting the availability of critical components such as semiconductors.
2. Global Pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how a global health crisis could cripple supply chains. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and workforce shortages caused by the pandemic disrupted manufacturing, shipping, and distribution. The just-in-time (JIT) inventory model, which many companies rely on for efficiency, was particularly vulnerable to the sudden surge in demand and supply shortages.
Pandemics can also create long-term disruptions, as seen with ongoing challenges in global shipping and semiconductor shortages caused by COVID-19-related factory shutdowns.
3. Geopolitical Tensions
Political instability, trade wars, tariffs, and economic sanctions can lead to supply chain disruptions, especially for companies that rely on international suppliers or operate in politically sensitive regions. Geopolitical tensions can disrupt shipping routes, delay the availability of materials, and increase costs due to tariffs and trade barriers.
For instance, the US-China trade war led to significant disruptions in the technology, automotive, and agricultural sectors, as companies had to navigate new tariffs and supply chain realignments.
4. Cyberattacks
The increasing reliance on digital technologies in supply chain management has made businesses more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers can disrupt logistics systems, steal sensitive data, and paralyze operations. In 2021, the ransomware attack on Colonial Pipeline in the US caused widespread fuel shortages and transportation disruptions, highlighting the potential for cyber threats to cripple critical supply chains.
5. Labor Strikes and Workforce Shortages
Labor strikes, protests, and workforce shortages can also disrupt supply chains, particularly in industries that rely on a stable labor force for production and distribution. Truck driver shortages, warehouse worker strikes, and port congestion can lead to significant delays in moving goods from one point to another.
6. Supplier Failures
When a key supplier goes out of business, faces financial difficulties, or experiences a major operational failure, it can create a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. Supplier dependency is a critical risk factor, particularly in industries with limited alternative sources for specialized components.
7. Transportation and Logistics Disruptions
Transportation is a critical link in the supply chain. Delays in shipping, port congestion, and limited freight capacity can all disrupt the timely delivery of goods. For instance, the 2021 blockage of the Suez Canal by the Ever Given container ship caused delays in global shipping for weeks, highlighting the vulnerability of supply chains to transportation bottlenecks.
Impacts of Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions can have significant financial and operational impacts on businesses and industries. Some of the key consequences include:
1. Production Delays
Disruptions in the availability of raw materials, components, or labor can halt production lines, leading to delays in manufacturing and assembly processes. This can cause missed deadlines, increased operational costs, and backlogs in fulfilling orders.
2. Increased Costs
Supply chain disruptions often lead to increased costs due to higher shipping rates, labor shortages, tariffs, and the need to source alternative materials or suppliers. These cost increases can affect profit margins and force businesses to pass on higher prices to consumers.
3. Inventory Shortages
When supply chain disruptions occur, businesses that rely on the just-in-time inventory model may find themselves facing inventory shortages, leading to stockouts and an inability to meet customer demand. This can damage a company’s reputation and result in lost sales.
4. Customer Dissatisfaction
Delayed deliveries, product shortages, and rising prices can lead to customer dissatisfaction, potentially causing long-term damage to a company’s brand and customer loyalty. In highly competitive markets, businesses that fail to deliver on time may lose customers to competitors.
5. Supply Chain Reconfiguration
In some cases, businesses may need to reconfigure their entire supply chain to mitigate the impact of disruptions. This could involve finding new suppliers, relocating manufacturing facilities, or restructuring logistics networks, all of which require time and resources.
How to Mitigate Supply Chain Disruptions
While supply chain disruptions are often unpredictable, businesses can take proactive steps to build resilience and mitigate their impact. Below are some key strategies for managing supply chain disruptions:
1. Diversify Suppliers
Relying on a single supplier or region for critical components is risky. Businesses should diversify their supplier base to include multiple suppliers across different regions. This ensures that if one supplier is unable to deliver, alternatives are available to keep production running.
2. Increase Supply Chain Visibility
Supply chain visibility refers to the ability to track and monitor goods, materials, and shipments throughout the entire supply chain. By implementing advanced technology such as real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and AI-powered supply chain management systems, businesses can identify potential disruptions before they escalate.
3. Build Inventory Buffers
While just-in-time inventory models are efficient, they leave businesses vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. To mitigate this risk, companies can build strategic inventory buffers, also known as safety stock, to ensure that they have enough materials on hand to continue production in the event of a disruption.
4. Develop Contingency Plans
Having a comprehensive contingency plan is essential for dealing with supply chain disruptions. This plan should outline the steps businesses will take to manage potential disruptions, such as rerouting shipments, engaging alternative suppliers, or shifting production to other locations.
5. Strengthen Supplier Relationships
Strong relationships with suppliers can improve communication and collaboration during disruptions. Businesses should work closely with suppliers to develop joint contingency plans, share information, and coordinate responses to potential disruptions.
6. Invest in Technology
Technology can play a critical role in supply chain resilience. Investing in digital tools like blockchain, AI, machine learning, and cloud-based supply chain management platforms can improve transparency, speed up decision-making, and enable businesses to respond quickly to disruptions.
7. Monitor Global Risks
Businesses should stay informed about global risks that could impact their supply chains, including geopolitical tensions, trade regulations, and environmental risks. Regularly monitoring these risks allows companies to prepare for potential disruptions and adjust their supply chain strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
Supply chain disruptions are an inevitable challenge for businesses in today’s interconnected global economy. From natural disasters to pandemics, cyberattacks, and geopolitical tensions, disruptions can arise from numerous sources, often with little warning. However, by understanding the causes and impacts of these disruptions and implementing strategies to build resilience, businesses can minimize their effects and ensure continued operations.
By diversifying suppliers, increasing visibility, building inventory buffers, and leveraging technology, businesses can create more flexible and agile supply chains that are better equipped to handle the unexpected. In a world where disruptions are becoming more frequent and complex, a proactive approach to supply chain management is critical for long-term success.
FAQs
1. What are supply chain disruptions?
Supply chain disruptions refer to any unexpected event or circumstance that halts or hinders the normal flow of goods, materials, or services within a supply chain. These disruptions can occur at any stage, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to consumers.
2. How do natural disasters impact supply chains?
Natural disasters can damage infrastructure, delay transportation, disrupt production, and create shortages of materials. For example, a hurricane can close ports or damage factories, leading to shipment delays and material shortages that ripple through the supply chain.
3. What was the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global supply chains?
The COVID-19 pandemic caused widespread disruptions, including factory shutdowns, shipping delays, labor shortages, and a sudden surge in demand for certain products. It exposed the vulnerabilities of global supply chains, especially in industries reliant on just-in-time (JIT) inventory models.
4. How can geopolitical tensions disrupt supply chains?
Geopolitical tensions, such as trade wars, tariffs, or sanctions, can lead to increased costs, restricted access to key materials, and delays in shipments. For example, tariffs imposed during the US-China trade war impacted industries reliant on Chinese suppliers, increasing costs and forcing companies to find alternative suppliers.
5. What role do cyberattacks play in supply chain disruptions?
Cyberattacks can paralyze supply chains by targeting logistics systems, disrupting communication, stealing data, or halting production lines. For instance, the 2021 ransomware attack on Colonial Pipeline disrupted fuel supply chains in the US, highlighting the risk of cyber threats.
Post a Comment